# 数据结构:2-3树
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
不讲红黑树,先讲2-3树里呢?
原本是想AVL树 (opens new window)讲解了左旋、右旋的操作,有了这样的基础就进入到红黑树的讲解,因为它们都是依靠旋转来调衡树高的。但红黑树的五条限定规则来的那么突然,没有原因,没有道理。
这时候大部分资料会用2-3树来讲解红黑树,不过又不去实现一个2-3树,只是用了一个理论套另外一个理论。虽然能从理解上多一些参考,但始终感觉没有抓手呀。对于理科思维来说,你得给我东西呀。老是整这悬得楞的🥶谁能受了。所以这里我们先来用Java实现一个2-3树,有了基础再学习红黑树
# 二、2-3树数据结构
2–3树是一种树型数据结构,由约翰·霍普克洛夫特于1970年发明。它通过在一个节点存放1-2个元素来平衡树高。从而也使2-3树存在2叉节点和3叉节点。
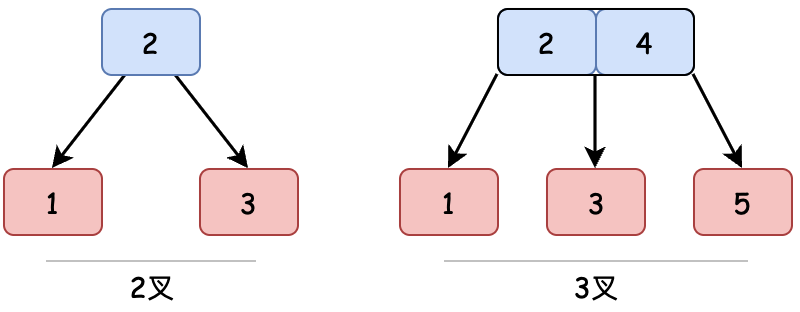
这里要提到一点,在BST二叉搜索树可能退化成链表的基础上。引出了自平衡二叉树,也就是包括上一章实现的AVL树和Java API HashMap中用到的红黑树,它们都属于BalancedTree,也统称为B树,平衡的意思。
而本章实现的2-3树也是一种简单的平衡树,其中每个具有子节点(内部节点)的节点要么有两个子节点(2 节点)和一个数据元素,要么有三个子节点(3 节点)和两个数据元素。另外 2-3 树是3阶B 树,2-3-4 树是4阶B树。
在实现2-3树之前,先通过图稿演示下在2-3树中顺序插入1、2、3、4、5、6、7,七个元素时,2-3树的调衡处理。
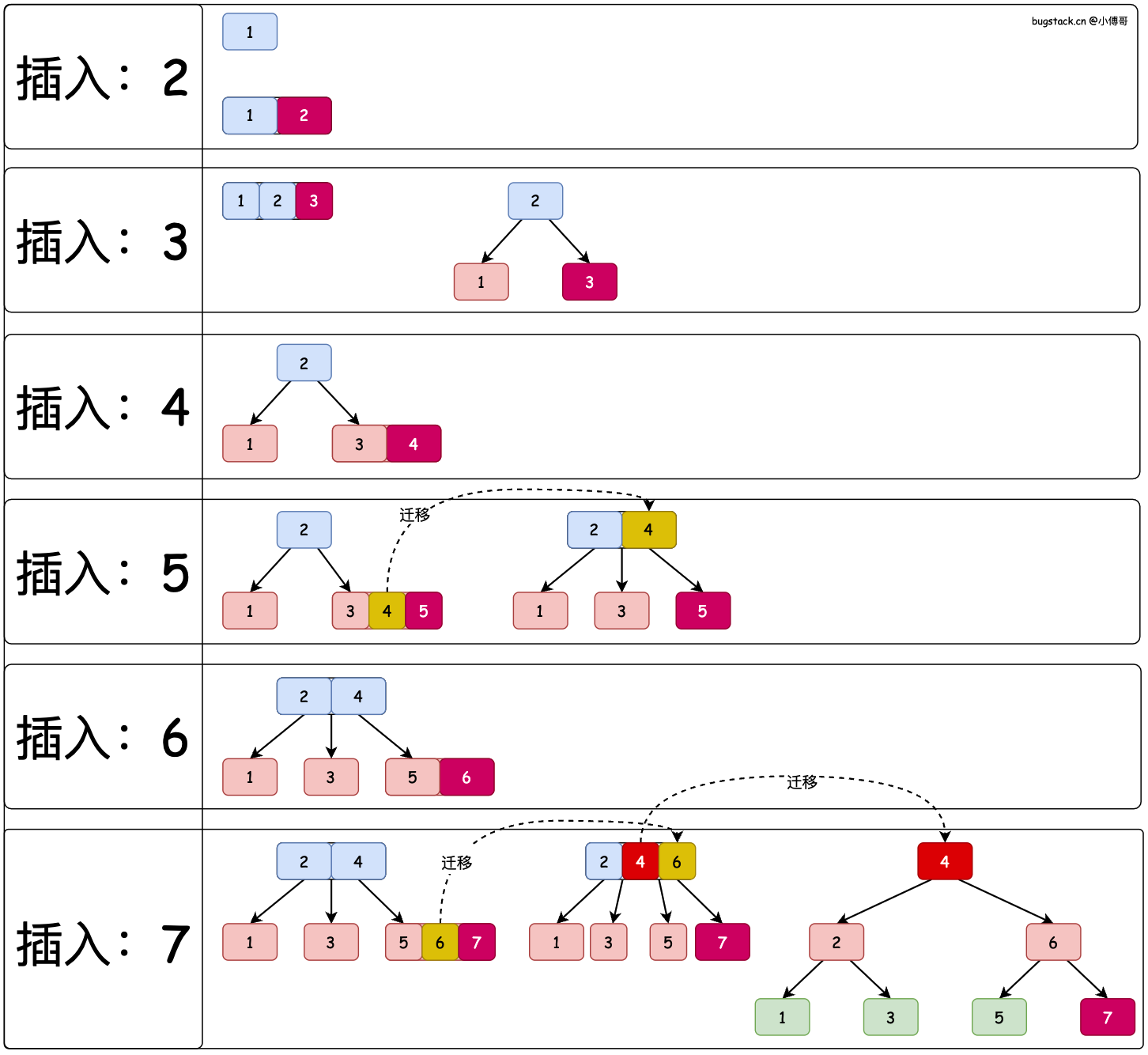
- 2-3 树的插入过程与 BST 树类似,会通过树的左右节点大小,找到自己的插入位置。
- 一个节点可以有1-2个元素(注意:不是1-3个),但当元素个数为3时,则需要调衡。把三个节点的中间节点晋升上来,其余两个节点为子节点。
- 如果进行一次调衡后,上一层父节点达到3个元素,则需要2次调衡,来满足2-3树的规则。
注意:2-3树的定义是每个节点可以有1-2个元素,当插入导致节点有3个元素时需要立即调衡。例如在插入节点9之前的树结构中,父节点6应该只有一个元素,其左子树为节点5。这样的结构符合2-3树的定义,也便于后续插入节点9时的调衡操作。
咋样,是不看过这个图之后对于2-3树的实现已经有感觉了,想动手写写试试了?
- 源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
- 本章源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms/tree/main/data-structures/src/main/java/tree (opens new window)
# 三、2-3树结构实现
2-3 树的实现并不复杂,但在实现前要思考🤔以下几个问题;
- Node 节点属性信息都包括什么?
- 插入值,是否需要创建新的 Node?
- 插入后,节点内有3个元素后,怎么迁移元素?
# 1. 节点定义
public class Node_2_3 {
// 元素
public int[] items;
// 序号
public int number;
// 孩子
public Node_2_3[] children;
// 父亲【非必须】
public Node_2_3 parent;
public Node_2_3() {
this.items = new int[3];
this.number = 0;
this.children = new Node_2_3[4];
this.parent = null;
}
public void insert(int e) {
int idx = this.number - 1;
while (idx >= 0) {
if (this.items[idx] < e) break;
this.items[idx + 1] = this.items[idx];
--idx;
}
this.items[idx + 1] = e;
++this.number;
}
// ... 省略部分代码
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 2-3树的几点元素需要包括;一个数组的元素集合、元素的序号、孩子元素。因为一个节点最多可临时放入3个元素,那么就会最多有4个孩子元素,所以孩子元素也是一个数组并且在构造函数中按照4个元素进行初始化。
- 由于本身2-3树插入元素的开始阶段,并不是直接创建一个新的节点,而是在初始化的数组空间中存入元素。所以在节点中提供了一个插入元素的方法 insert 来处理新增元素。
- 另外2-3树的节点类,还提供了一个方便查询的方法。包括:获取左边元素、中间元素、右边元素,以及最小值、最大值和判断是否有孩子节点。这些内容可以源码。
# 2. 拆分节点
当一个节点内有3个元素的时候,就要发起拆分东西,拆分的过程分为;
- 对3个节点的中间节点,插入到父节点上。
- 剩余2个节点创建出新的节点。
- 建立父节点和新创建的2个节点间关系。
整个操作流程如图所示
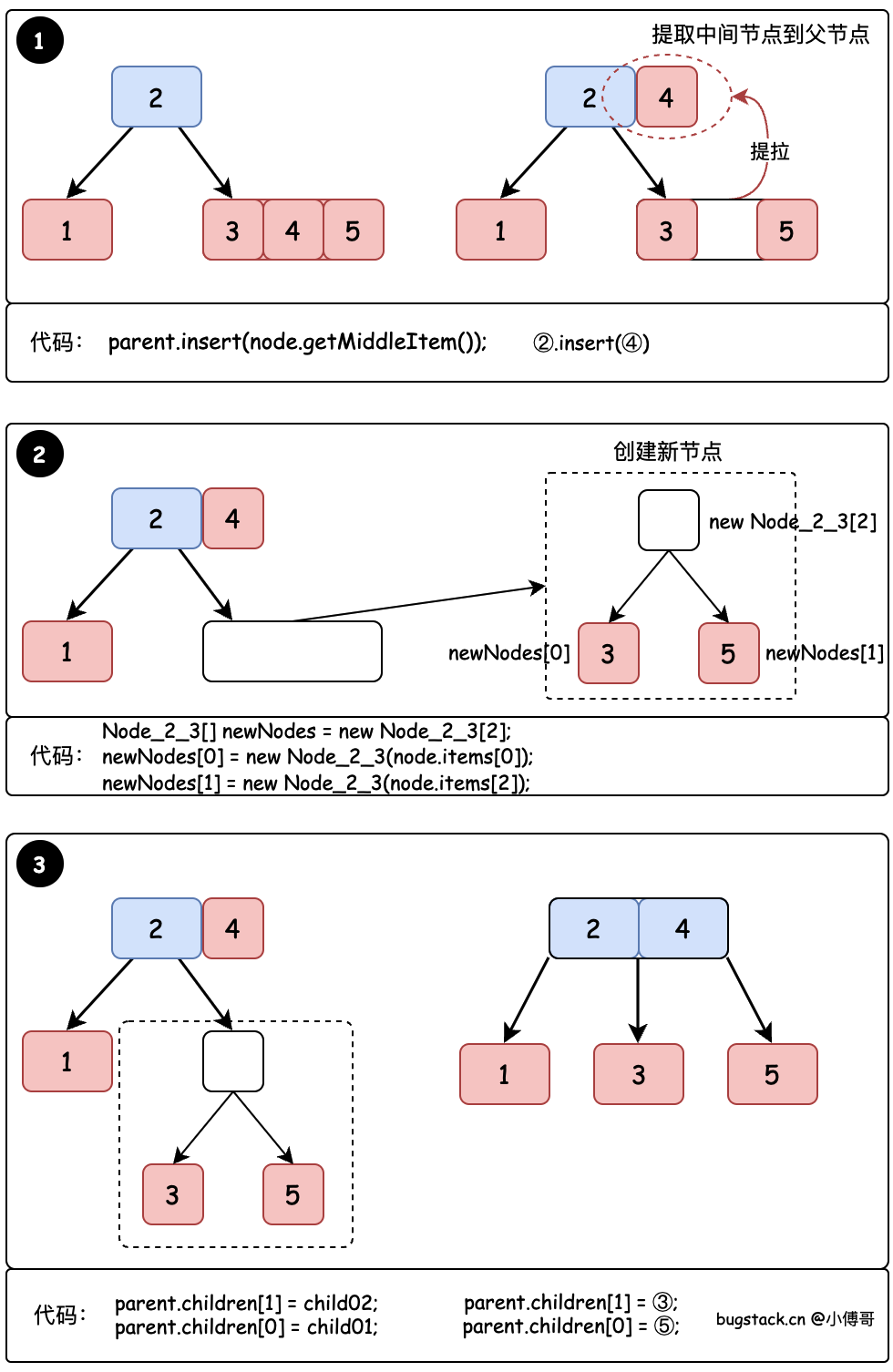
# 1. 插入父节点
private Node_2_3 split(Node_2_3 node, Node_2_3 parent) {
if (parent == null) {
parent = new Node_2_3(node);
}
parent.insert(node.getMiddleItem());
Node_2_3[] newNodes = this.triangle(node);
this.replaceChild(parent, node, newNodes[0], newNodes[1]);
return parent;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 整个2-3树拆分的过程就是在 split 这个方法里,第一步解决了是否有父节点,没有则创建。
- 之后将原节点的中间值插入到父节点中。接下来的操作就是拆分新节点和更换孩子节点建立新连接。
# 2. 拆分新节点
private Node_2_3[] triangle(Node_2_3 node) {
Node_2_3[] newNodes = new Node_2_3[2];
newNodes[0] = new Node_2_3(node.items[0]);
newNodes[1] = new Node_2_3(node.items[2]);
if (!node.isLeaf()) {
// 左孩子
newNodes[0].children[0] = node.children[0];
newNodes[0].children[1] = node.children[1];
// 右孩子
newNodes[1].children[0] = node.children[2];
newNodes[1].children[1] = node.children[3];
}
return newNodes;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 基于传递进来的节点,将节点的左右孩子创建新节点,如果这个孩子节点还有分支节点,则一并更新。
# 3. 建立新连接
private void replaceChild(Node_2_3 parent, Node_2_3 oldChild, Node_2_3 child01, Node_2_3 child02) {
if (oldChild == parent.children[0]) {
parent.children[3] = parent.children[2];
parent.children[2] = parent.children[1];
parent.children[1] = child02;
parent.children[0] = child01;
} else if (oldChild == parent.children[1]) {
parent.children[3] = parent.children[2];
parent.children[2] = child02;
parent.children[1] = child01;
} else {
parent.children[3] = child02;
parent.children[2] = child01;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 建立新连接需要判断这个节点 oldChild 是父节点的左、中、右,之后进行依次的更换。
- 如拆分节点的介绍图中,用到的就是
parent.children[1] = child02;parent.children[0] = child01;两步操作过程。
# 3. 新增节点
public void insert(int e) {
// 记录元素
elementList.add(e);
// 插入元素
if (root == null) {
root = new Node_2_3(e);
} else {
root = insert(e, root);
if (root.number == 3) {
root = split(root, null);
}
}
}
private Node_2_3 insert(int e, Node_2_3 parent) {
if (parent.isLeaf()) {
parent.insert(e);
return parent;
}
Node_2_3 child = null;
if (parent.number == 1) {
if (e < parent.getMinItem()) {
child = insert(e, parent.getLeft());
} else {
child = insert(e, parent.getMiddle());
}
} else {
if (e < parent.getMinItem()) {
child = insert(e, parent.getLeft());
} else if (e > parent.getMiddleItem()) {
child = insert(e, parent.getRight());
} else {
child = insert(e, parent.getMiddle());
}
}
if (child.number == 3) {
return this.split(child, parent);
}
return parent;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
- 新增节点的过程就比较简单了,一种是使用递归找到可以插入的位置,另外一种就是 where 循环。我们再BST、AVL两种数据结构种都是用了 where 循环。
- 在2-3树中 insert 方法递归到对应的插入位置后,开始插入元素。当插入元素结束后判断这个节点是否已经达到了3个节点,如果是则进行拆分。拆分就调用了上面的步骤
# 四、2-3树结构测试
为了让读者更好的理解2-3树的结构,小傅哥在程序的控制台打印了插入的过程。网上没有2-3树在线的动画演示,如果读者看到也可以留言给小傅哥
@Test
public void test_insert_incr() {
Tree_2_3 tree = new Tree_2_3();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
tree.insert(i);
System.out.println(tree);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 顺序插入10个节点,如果这是一颗BST树,它将会退化成链表。那么我们使用自平衡的2-3树,来看看它的插入效果。
测试效果
输入节点(1个):1
[1]
输入节点(2个):1,2
[1,2]
输入节点(3个):1,2,3
/----- [3]
[2]
\----- [1]
输入节点(4个):1,2,3,4
/----- [3,4]
[2]
\----- [1]
输入节点(5个):1,2,3,4,5
/----- [5]
[2,4]---- [3]
\----- [1]
输入节点(6个):1,2,3,4,5,6
/----- [5,6]
[2,4]---- [3]
\----- [1]
输入节点(7个):1,2,3,4,5,6,7
/----- [7]
/----- [6]
| \----- [5]
[4]
| /----- [3]
\----- [2]
\----- [1]
输入节点(8个):1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
/----- [7,8]
/----- [6]
| \----- [5]
[4]
| /----- [3]
\----- [2]
\----- [1]
输入节点(9个):1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
/----- [9]
/----- [6,8]---- [7]
| \----- [5]
[4]
| /----- [3]
\----- [2]
\----- [1]
输入节点(10个):1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
/----- [9,10]
/----- [6,8]---- [7]
| \----- [5]
[4]
| /----- [3]
\----- [2]
\----- [1]
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
- 有了这样的数据结构示意,是不是再来看2-3树就非常清晰了。—— 我说过,理科生 + 技术,不要只抛理论,要看效果的!东西到手了,能拿捏了,再补充理论。
# 五、常见面试问题
- 2-3树的数据结构描述
- 2-3树一个节点最多可以存放几个元素
- 2-3树插入节点时间复杂度
- 2-3树一个节点有3个元素,如何迁移。需要旋转吗
- 2-3树,你能手写一下吗?

